GE VMIVME-5576 Fiber-Optic Reflective Memory with Interrupts
VMIVME-5576
Fiber-Optic Reflective Memory with Interrupts
High-speed, easy-to-use fiber-optic network (170 Mbaud serially)
Data written to memory in one node is also written to memory in all nodes on
the network
Up to 2.000 m between nodes and up to 256 nodes
Data transferred at 6.2 Mbyte/s without redundant transfer
Data transferred at 3.2 Mbyte/s with redundant transfer
Any node on the network can generate an interrupt in any other node on the
network or in all network nodes with a single command
Error detection
Redundant transmission mode for suppressing errors
No processor overhead
No processor involvement in the operation of the network
Up to 1 Mbyte of Reflective Memory
A24:A32:D32:D16:D8 memory access
Single 6U VMEbus board
INTRODUCTION
VMIVME-5576 is a
high-performance, multidrop VME-to-VME network. Data is
transferred by writing to on-board global RAM. The data is
automatically sent to the location in memory on all Reflective
Memory boards on the network.
PRODUCT OVERVIEW
—
The Reflective Memory
concept provides a very fast and efficient way of sharing data
across distributed computer systems.
VMIC’s VMIVME-5576 Reflective Memory interface
allows data to be shared between up to 256 independent
systems (nodes) at rates up to 6.2 Mbyte/s. Each Reflective
Memory board may be configured with 256 Kbyte to 1 Mbyte
of on-board SRAM. The local SRAM provides fast Read
access times to stored data. Writes are stored in local SRAM
and broadcast over a high-speed fiber-optic data path to other
Reflective Memory nodes. The transfer of data between nodes
is software transparent, so no I/O overhead is required.
Transmit and Receive FIFOs buffer data during peak data
rates to optimize CPU and bus performance to maintain high
data throughput.
The Reflective Memory also allows interrupts to one or
more nodes by writing to a byte register. These interrupt (three
level, user definable) signals may be used to synchronize a
system process, or used to follow any data that may have
preceded it. The interrupt always follows the data to ensure the
reception of the data before the interrupt is acknowledged.
The VMIVME-5576 requires no initialization unless
interrupts are being used. If interrupts are used, vectors and
interrupt levels must be written to on-board registers and the
interrupts armed.
Each node on the system has a unique identification
number between 0 and 255. The node number is established
during hardware system integration by placement of jumpers
on the board. This node number can be read by software by
accessing an on-board register. In some applications, this node
number would be useful in establishing the function of the
node.
LINK ARBITRATION — The VMIVME-5576 system
is a fiber-optic daisy chain ring as shown in Figure 2. Each
transfer is passed from node to node until it has gone all the
way around the ring and reaches the originating node. Each
node retransmits all transfers that it receives except those that
it had originated. Nodes are allowed to insert transfers
between transfers passing through.
INTERRUPT TRANSFERS — In addition to
transferring data between nodes, the VMIVME-5576 will
allow any processor in any node to generate an interrupt on
any other node. These interrupts would generally be used to
indicate to the receiving node that new data has been sent and
is ready for processing. These interrupts are also used to
indicate that processing of old data is completed and the
receiving node is ready for new data.
Three interrupts are available. The user may define the
function, priority, and vector for each interrupt. Any
processor can generate an interrupt on any other node on the
network. In addition, any processor on the network can
generate an interrupt on all nodes on the network. Interrupts
are generated by simply writing to a single VMIVME-5576
register.
All data and interrupt command transfers contain the
node number of the node that originated the transfer. This
information is used primarily so the originating node can
remove the transfer from the network after the transfer has
traversed the ring. The node identification is also used by
nodes receiving interrupt commands. When a node receives
an interrupt command for itself, it places the identification
number of the originating node in a FIFO. Up to 512
interrupts can be stacked in the FIFO. During the interrupt
service routine, the identification of the interrupting node can
be read from the FIFO.
ERROR MANAGEMENT — Errors are detected by
the VMIVME-5576 with the use of the error detection
facilities of the TAXI chipset and additional parity encoding
and checking. The error rate of the VMIVME-5576 is a
function of the rate of errors produced in the optical portion
of the system. This optical error rate depends on the length
and type of fiber-optic cable.
Assuming an optical error rate of 10-12. the error rate of
the VMIVME-5576 is 10-10 transfers/transfer. However, the
rate of undetectable errors is less than 10-20 transfers/transfer.
When a node detects an error, the erroneous transfer is
removed from the system and a VMEbus interrupt is
generated, if armed.
The VMIVME-5576 can be operated in a redundant
transfer mode in which each transfer is transmitted twice. In
this mode of operation, the first of the two transfers is used
unless an error is detected in which case the second transfer
is used. In the event that an error is detected in both transfers,
the node removes the transfer from the system. The
probability of both transfers containing an error is 10-20. or
about one error every 372.000 years at maximum data rate.
PROTECTION AGAINST LOST DATA — Data
received by the node from the fiber-optic cable is error
checked and placed in a receive FIFO. Arbitration with
accesses from the VMEbus then takes place and the data is
written to the node’s SRAM and to the node’s transmit FIFO.
Data written to the board from the VMEbus is placed directly
into SRAM and into the transmit FIFO. Data in the transmit
FIFO is transmitted by the node over the fiber-optic cable to
the next node. Data could be lost if either FIFO were allowed
to become full.
The product is designed to prevent either FIFO becoming
full and overflowing. It is important to note the only way that
data can start to accumulate in FIFOs is for data to enter the
node at a rate greater than 6.2 or 3.2 Mbyte/s in redundant
mode. Since data can enter from the fiber and from the
VMEbus, it is possible to exceed these rates. If the transmit
FIFO becomes half-full, a bit in the Status Register is set and,
if armed, an interrupt is generated. This condition is an
indication to the software in the node that writes to the
Reflective Memory should be suspended until the FIFO
becomes less than half-full. If the half-full indication is
ignored and the transmit FIFO becomes full, then writes to the
Reflective Memory will be acknowledged with a bus error.
With VMEbus writes being blocked by the bus error, data
cannot overflow in the receive FIFO.
NETWORK MONITOR — There is a bit in a Status
Register that can be used to verify that data is traversing the
ring (that is, the ring is not broken). This can also be used to
measure network latency.
SPECIFICATIONS
Memory Size: 256 Kbyte, 512 Kbyte, or 1 Mbyte
Access Time:
400 ns (worst-case arbitration)
200 ns (best-case arbitration)
TRANSFER SPECIFICATION
Transfer Rate:
6.2 Mbyte/s (longword accesses) without redundant
transfer
3.2 Mbyte/s (longword accesses) with redundant transfer
COMPATIBILITY
VMEbus: This product complies with the VMEbus
specification (ANSI/IEEE STD 1014-1987. IEC 821 and
297), with the following mnemonics:
A32: A24: D32/D16/D08 (EO): Slave: 39/3D:09/0D
Form factor: 6U
Memory: Addressable on 256 Kbyte boundaries for
256 Kbyte memory option
Addressable on 512 Kbyte boundaries for 512 Kbyte
memory option
Addressable on 1 Mbyte boundary for 1 Mbyte memory
option
INTERCONNECTION
Cable Requirements: Two fiber-optic cables
Cable Length: 2.000 m maximum between nodes
Configuration: Daisy chain ring up to 256 nodes
PHYSICAL/ENVIRONMENTAL
Temperature Range: 0 to 55 °C, operating-40 to 85 °C, storage
Relative Humidity: 20 to 80 percent, noncondensing
Power Requirements: 5.0 A maximum at +5 VDC
MTBF: 142.400 hours (217F)
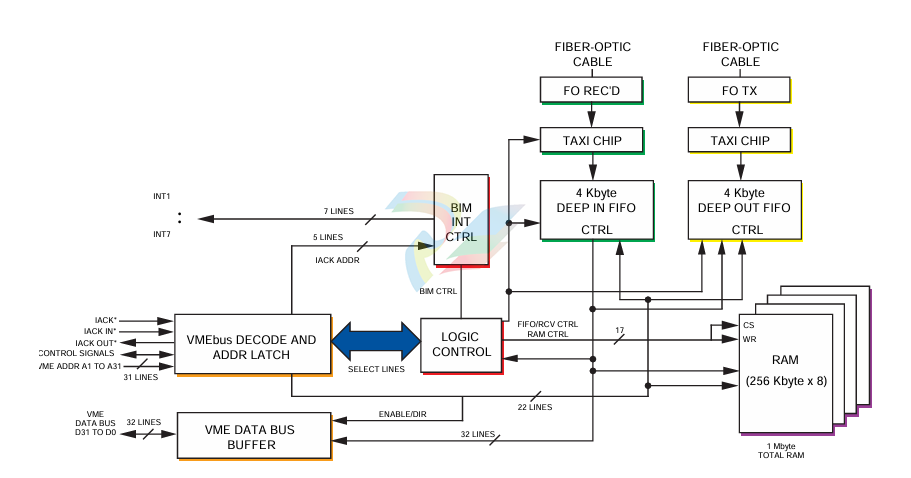
DATA TRANSFERS
Data written into the Reflective Memory is broadcast to
all nodes on the network without further involvement of the
sending or receiving nodes. Data is transferred from memory
locations on the sending nodes to corresponding memory
locations on the receiving nodes.
A functional block diagram of the VMIVME-5576 is
shown in Figure 1.
TRADEMARKS
The VMIC logo is a registered trademark of VMIC.
Other registered trademarks are the property of their
respective owners.
-
UniOP eTOP308 ETOP308U301 HMI Panel
-
UniOP ePALM10-0061 Handheld Robot Trainer
-
UniOP CP01R-04 CP05R-04 and CP01F-02
-
Uniop MD02R-04 - MD02R-04-0045 Industrial PLC Workstation
-
Uniop Cp02r-04-0021 Operating Interface
-
UniOP ECT-16-0045 High-Performance Color Touchscreen HMI
-
UniOP ERT-16 - Industrial PLC Workstation
-
UniOP ePAD04-0046 Compact Industrial Interface
-
UniOP BKDR-16 High-Reliability Monochrome Operator Interface
-
UniOP MKDR-04-004 Control Unit Panel
-
UniOP eTOP515 Series 500 HMI
-
Woodward 9907-1199 Advanced CPC-II Current-to-Pressure Converter
-
Woodward 8200-1300 High-Precision 505D Steam Turbine Controller
-
ABB PFSK130 3BSE002616R1 Core Signal Conditioning Unit
-
ABB PFSK165 3BSE027778R1 VP74201-933CW07 Signal Processing and Communication Unit
-
ABB PFSK164 3BSE021180R1 Tension sensor module and processing board
-
ABB 3BSE006505R1 PFSK142 Control board
-
ABB PFSK160A 3BSE009514R1 Regulated High-Capacity 24V DC
-
ABB PFSK162 3BSE015088R1 Signal Conditioning and Processing Board
-
ABB PFSK152 3BSE018877R1 Signal concentrator board
-
ABB PFSK151 3BSE018876R1 High-performance signal processing unit
-
ALSTOM PIB1201A 3BEC0067 Power Interface Board (PIB)
-
ALSTOM PIB310 3BHB0190 Adapter Module / Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
-
ALSTOM PIB102A 3BEB0180 Communication Card / PCB Module
-
ALSTOM BGTR8HE 24491276A1004 High-Frequency Power Controller / Rack Module
-
ALSTOM LC105A-1 Digital Discrete Output (Relay)
-
ALSTOM IR139-1 High-Efficiency Inverter / Control Board
-
ALSTOM AM164 Analog Output / Remote I/O
-
ALSTOM LE109A-1 Power System Control and Monitoring Module
-
ALSTOM UT150-1 PID temperature controller / process control board
-
ALSTOM AL132 AL132A STO0982E01 Control Motherboard / CPU Card
-
ALSTOM AS111-1 Analog Output (AO) Module
-
WATLOW AH116-2 Servo Drive / Control Module
-
WATLOW V4555724-0100 Electromechanical Contactor /Power Switch
-
Alstom KCEU142 Digital Protection Relay
-
ALSTOM MMLG01 Test block
-
WATLOW 999D,999A Digital/Analog Dual-Channel Base Unit
-
WATLOW 998D 998A Digital/Analog Dual-Channel Base Unit
-
WATLOW 999D-11FF-AARG Dual-channel digital unit with universal process outputs
-
WATLOW Wattlo 998D-22KK-ARRG is a high-performance dual-channel digital controller
-
WATLOW 996A Single-loop controller
-
WATLOW 996D-11CC-CUGR Single-loop digital controller
-
WATLOW 996D Single-Channel Digital Temperature/Process Controller
-
WATLOW 997D Digital Dual-Channel Base Unit
-
WATLOW 997A Analog Dual-Channel Variant
-
WATLOW DAC / SDAC Digital-to-Analog / Serial-to-Analog Modules
-
WATLOW MLS300-OIT Operator Interface Terminal (Keypad/Display),Discontinued
-
WATLOW CIM300 Communication Interface Module (EIA-232/485),Discontinued
-
WATLOW MLS300-CIM Control Interface Module
-
WATLOW MLS300-AIM,Analog Input Module (16-channel expansion),Discontinued
-
WATLOW MLS300-PM Processor Module (Central CPU),Discontinued
-
Watlow MLS332 32-Loop Processor Base Unit,Discontinued
-
Watlow MLS316 Multi-loop thermal controller
-
Watlow CLS208 C10000CP high-performance, 8-loop PID temperature controller
-
Watlow CAS 16CLS/CAS Multi-loop temperature controller
-
ABB CP555 1SBP260179R1001 Product Overview
-
Watlow MLS300 Multi-Loop Control System
-
Watlow 997D-11CC-JURG SERIES 997 Vertical Limit Control
-
Watlow CLS216 Multi-Loop PID Temperature Controller
-
Watlow NLS300-CIM316 Multi-Loop Control Interface Module
-
Watlow PPC-TB50 (30280-00) Precision Power Controller
-
ABB 3BSE014227R1 RF533 Central Unit
-
WOODWARD 5448-890 SPM-D10 Series One Breaker Synchronizer
-
FOXBORO 43AP-FA42D/PB-AA 43AP Pneumatic Indicating Controllers
-
Stucke Elektronik SYMAP®G generator protection
-
Stucke Elektronik SYMAP®F feeder protection
-
Stucke Elektronik SYMAP®ECG engine control and generator protection
-
Stucke Elektronik SYMAP®EC Engine Control
-
Stucke Elektronik SYMAP®ARC Arc protection system
-
Stucke Elektronik SYMAP®R Digital protection system
-
Stucke Elektronik SYMAP® Compact Digital protection and control equipment
-
LEYBELOD SV40 BI Single-stage, oil-sealed rotary vane pump
-
LEYBELOD TURBOVAC 361 (C) Suspension turbomolecular pump
-
LAND M2300/1100C-V Industrial Control Module
-
LAMBDA LZS-1500-3 Single Output Industrial Power Supplies
-
LAMBDA LZS-A1500-3-001 POWER SUPPLY
-
LAMBDA HWS1500-24 Power supply
-
Kongsberg K-Chief Control Room Panel (CRP) 603525
-
Kongsberg MSI-12 Input/Output Module 339368
-
Kongsberg dPSC Dual Process Segment Controller Module 8100183
-
HHirschmann Modular OpenRail Fast Ethernet switch 8-24 ports MS20-1600SAAEHH08.0
-
Hirschmann MM20-Z6Z6Z6Z6SAHH ETHERNET / Fast-ETHERNET Media Modules
-
Hirschmann MM2-2FXM3/2TX1 ETHERNET / Fast-ETHERNET Media Modules
-
Hirschmann Industrial ETHERNET Switch MICE MS20/MS30
-
Hirschmann MACH102-24TP-FR Gigabit Ethernet industrial workgroup switch
-
Hirschmann MM2-4TX1 MICE switch medium module
-
Hirschmann MICE switch medium module MM2-2FXS2
-
ABB AFS670 19" Ruggedized Switch AFS670-EREEDDDSSEEEEEEEPZYX05.1.0
-
NI Controller for VXI VXIPC-871B
-
GE VMIVME-1150 Serial Communications Controller
-
GE Hydran M2-X Enhanced Monitoring with Extended Sensor Life
-
GE IC660BBD022 I/O module
-
GE Digital Energy D20 Analog Input Module
-
Foxboro FBM I/O cards PBCO-D8-009
-
GE SR750-P5-G5-S5-HI-A20-R-E Multilin Relay
-
ABB 3BSE019050R1000 PFTL 301E 1,0kN, Load cell
-
Foxboro DNBT P0971WV Dual-node bus module of I/A series
-
EPRO MMS6210 Dual-channel axial displacement measurement module
-
EMERSON PMCspan PMC Expansion Mezzanine
-
EMERSON KJ3242X1-BK1 12P4711X042 S-Series H1 Card
-
EMERSON KJ4006X1-BD1 Interface Terminal Block
-
EMERSON KJ4001X1-CK1 40-Pin Mass Termination Block
-
ABB UCD224A103 Industrial controller module
-
ABB ARCOL 0339 Solid-state motor controller
-
ABB UFC718AE01 HIEE300936R0101 Main Circuit Interface Board
-
Abaco VME-REPEATL-485 VMEBus Repeaters
-
Abaco VME-4900 Digital-to Synchro/Resolver Board
-
Abaco VME-4911 digital converter board
-
Abaco XM-664-80 Transition module with rear I/O access to VIPC664
-
Abaco TPMCC 6U VME triple PMC carrier for use with the V5C SBC
-
Abaco VIPC8243 is an intelligent 6U VME carrier board
-
Abaco DCPMC Conduction-cooled or Rugged PMC Carrier
-
Abaco CP237 is a 6U CompactPCI Card
-
Abaco VME-3413 32-Channel Signal Conditioning Board
-
Abaco VME-3125 VME Analog I/O Input Boards
-
Alstom GE SPU232.2. 029.366.817 Single Processor Unit SPU2322
-
ALSTOM COP232.2 VME A32/D32, 029.232 446 controller unit
-
ICS TRIPLEX T8111C Trusted TMR Processor
-
VMIC VMIVME-7740 VME Single Board Compute 750
-
foxboro FBM232 Field Device System Integrator Module P0926GW
-
GE 04220HL21204A IPC Control Module
-
ABB 3BSE000860R1 SB510 Backup Power
-
ABB 0504994880 Controller unit
-
ABB PFSA140 3BSE006503R1 Industrial robot Supply Unit
-
ABB 5SHX1445H0002 3BHL000387P0101 POWER IGCT unit
-
ABB 128877-103 CABLE, SP1200 IR DET.
-
ABB CI853K01 and TP853 RS-232C Interface
-
ABB REM610 MOTOR PROTECTION RELAY REM610C11HCNR
Add: High-tech Software Park, Xiamen City, Fujian Province
Mobile: +86-17750019513(WhatsApp)
Email: yy4291644@gmail.com
Website: https://www.abb-sis.com

-
UniOP eTOP308 ETOP308U301 HMI Panel
-
UniOP ePALM10-0061 Handheld Robot Trainer
-
UniOP CP01R-04 CP05R-04 and CP01F-02
-
Uniop MD02R-04 - MD02R-04-0045 Industrial PLC Workstation
-
Uniop Cp02r-04-0021 Operating Interface




.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)