Pressductor Pillowblock Load Cells Vertical Measuring PFCL 201 User manual
USE OF SYMBOLS
This publication includes the following symbols with information regarding safety or other important information:
CAUTION Caution icon indicates important information. Risk of damage to equipment, property or software.
DANGER Danger icon indicates a hazard which could result in personal injury or even death.
ELECTRICAL Electrical warning icon indicates the presence of a hazard which could result in electrical shock.
ESD ESD icon indicates that electrostatic discharge precautions are needed.
Information Information icon alerts the reader to relevant facts and conditions.
Tip Tip icon advise how to design your product or how to use a certain function.
NOTICE
The information in this document is subject to change without notice and should not be construed as a commitment by ABB AB. ABB AB assumes no responsibility for any errors that may appear in this document.
In no event shall ABB AB be liable for direct, indirect, special, incidental or consequential damages of any nature or kind arising from the use of this document, nor shall ABB AB be liable for incidental or consequential damages arising from use of any software or hardware described in this document.
This document and parts thereof must not be reproduced or copied without ABB AB’s written permission, and the contents thereof must not be imparted to a third party nor be used for any unauthorized purpose. The software described in this document is furnished under a license and may be used, copied, or disclosed only in accord ance with the terms of such license.
Description
General
The load cell is machined from a single piece of stainless steel. The sensors are machined directly in the piece of steel and are positioned so that they are sensitive to force in the direction of meas urement and insensitive in other directions.
The load cell is mounted on a base with four screws, and the bearing housing is mounted on top of the load cell with four screws.
Every load cell comes calibrated and temperature compensated.
The load cells PFCL 201C/201CE/201CD are available in four measurement ranges, all variants have the same external dimensions.
The load cell PFCL 201C is equipped with a connector for the pluggable connection cable. The load cell PFCL 201CE has a fixed connection cable with protective hose. The load cell PFCL 201CD is provided with an acid-proof cable gland with a fixed PTFE- insulated connection cable.
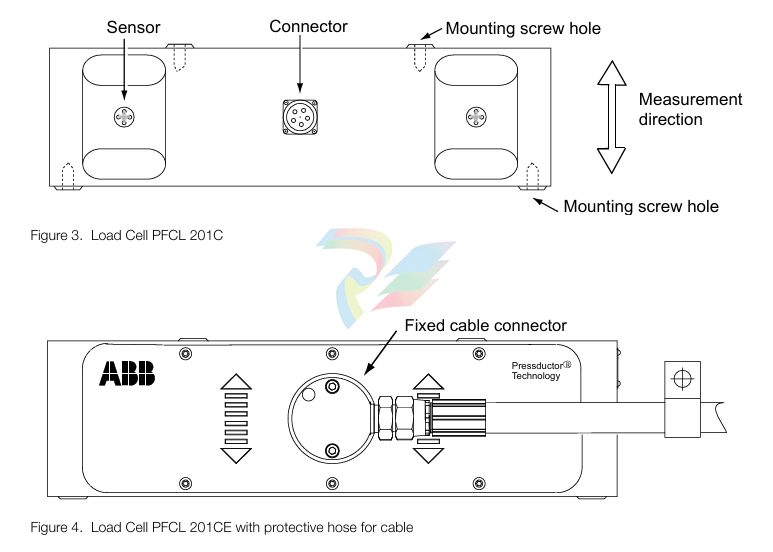
Definitions
Nominal load
Nominal load, Fnom, is the maximum load in the measurement direction for which the load cell is dimensioned to measure within the specified accuracy class. The load cell is calibrated up to Fnom.
Sensitivity
Sensitivity is defined as the difference in output values between nominal load and zero load.
Accuracy and Accuracy Class
Accuracy class is defined as the maximum deviation, and is expressed as a percentage of the sen sitivity at nominal load. This includes linearity deviation, hysteresis and repeatability error.
Linearity Deviation
Linearity deviation is the maximum deviation from a straight line drawn between the output values at zero load and nominal load. Linearity deviation is related to the sensitivity.
Hysteresis
Hysteresis is the maximum difference in the output signal at the same load during a cycle from zero load to nominal load and back to zero load, related to the sensitivity at nominal load. The hysteresis of a Pressductor transducer is proportional to the load cycle.
Repeatability error
Repeatability error is defined as the maximum deviation between repeated readings under identical conditions. It is expressed as a percentage of the sensitivity at nominal load.
Compensated temperature range
The temperature drifts of the load cell have been compensated for in certain temperature ranges. That is the temperature range within which the specified permitted temperature drifts (i.e. zero point and sensitivity drifts) of the load cell are maintained.
Working temperature range
Working temperature range is the temperature range within which the load cell can operate within a specified accuracy. The maximum permitted temperature drifts (i.e. zero point and sensitivity drifts) of the load cell are not necessarily maintained in the whole working temperature range.
Storage temperature range
Storage temperature range is the temperature range within which the load cell can be stored.
Zero point drift with temperature
Zero point drift is defined as the signal change with temperature, related to the sensitivity, when there is zero load on the load cell.
Sensitivity drift with temperature
Sensitivity drift is defined as the signal change with temperature at nominal load, related to the sen sitivity, excluding the zero point drift.
Compression
Compression is the total reduction in the height of the load cell when the load is increased from zero to the nominal value.
Measuring principle of the sensor
The measuring principle of the sensor is based on the Pressductor® technology and the fact that the permeability of a magnetic material changes under mechanical stress.
The sensor is a membrane machined in the load cell. Primary and secondary windings are wound through four holes in the load cell so that they cross at right angles.
-
Woodward easYgen-3200-1/P1 8440-2049
-
Woodward easYPROTEC-1410-7 8441-1161 8441-1160
-
Woodward MFR300-71M/K45 8444-1111 8444-1112
-
Woodward MFR300-75M 8444-1107 8444-1108 8444-1109
-
Woodward MFR300-71M/K42 8444-1104
-
Woodward MFR300 75M/SU03, Transducer 8444-1093 8444-1094 8444-1095
-
Woodward MFR300-71M 8444-1091 8444-1092
-
Woodward MFR300-15M 8444-1090 8444-1089
-
Woodward MFR300-11M 8444-1071 8440-1089
-
Woodward MFR500-6M/WK0400 + DPC USB 8444-1070
-
Woodward MFR300-15M 8444-1064
-
Woodward SPM-D2-1040B/NYB 8440-2189
-
Woodward SPM-D2-1010B/NYB 8440-2177
-
Woodward SPM-D2-10B/PSY5-FU-D 8440-2170
-
Woodward SPM-D2-1040B/XN analog speed/voltage bias 8440-2190
-
Woodward MFR300-71M 8444-1063
-
SPM-D2-1010B/X analog speed/voltage bias 8440-2168
-
Woodward SPM-D2-1040B/X analog speed/voltage bias 8440-2171
-
Woodward SPM-D2-1010B/N wide range power supply 8440-2174
-
Woodward SPM-D2-1040B/N wide range power supply 8440-2175
-
Woodward SPM-D2-1010B /110VAC sensing 8440-2166
-
Woodward SPM-D2-1040B /400VAC sensing 8440-2164
-
Woodward DTSC-200A 8440-2297
-
Woodward DTSC-200-55B/K38 8440-2155
-
Woodward DTSC-200-51B 8440-1867 8440-1868
-
Woodward 8445-1049 8445-1048 Converter, 1x FO to CAN
-
Woodward easYlite-200 8446-1007 LED Lamp Expansion Module
-
Woodward IKD-OUT-16 16 DO Expansion Card 8440-2306
-
Woodward IKD-IN-16 16 DI Expansion Card 8440-2307
-
Woodward IKD1M 8 DI/8 DO Expansion Card 8440-2116
-
Woodward easYview-07-30 8446-1071
-
Woodward easYFLEX-3400XT-P2 (GAP) 8440-2217
-
Woodward easYFLEX-3400XT-P2 (GAP) 8440-2217
-
Woodward easY-I-3400XT-P1 8440-2293
-
Woodward easY-I-3500XT-P1 8440-2292
-
Woodward MSLC-2XT 8440-2298 Master Synchronizer and Load Control
-
Woodward DSLC-2XT 8440-2299 Digital Synchronizer and Load Control
-
Woodward: GC-3400XT-P1 8440-2267 Group Controller
-
Woodward: LS-612XT-P2 8440-2317
-
Woodward: CONTROL-LS-612XT-P1,8440-2222 Cabinet back mounting
-
Woodward: LS-522-1/P1 8440-2179
-
Woodward: LS-522-5/P1 8440-2151
-
Woodward: LS-512-1/P1 8440-2181
-
Woodward: LS-512-5/P1 8440-2153
-
Woodward: LS-521-1/P1 8440-2178
-
Woodward: CONTROL-LS-521-5/P1 8440-2150
-
Woodward: LS-511-1/P1 8440-2180 Circuit Breaker Control & Protection
-
Woodward: CONTROL-LS-511-5/P1 8440-2152 Circuit Breaker Control & Protection
-
Woodward easYgen-3500XT-P2-LT-RENTAL 8440-2291 Genset Control for
-
Woodward eeasYgen-3500XT-P2-RENTAL 8440-2290
-
Woodward easYgen-3200XT-RENTAL 8440-2285
-
easYgen-3500XT-P2-K58 8440-2318
-
easYgen-3500XT-P2-LT 8440-2089
-
Woodward easYgen-3500XT-P2 8440-2088 Genset Controller
-
Woodward: easYgen-3500XT-P1-LT 8440-2086
-
Woodward: easYgen-3500XT (P1) 8440-2085
-
Woodward: easYgen-3400XT (P2), Genset Controller 1A/5A 8440-2087
-
Woodward: easYgen-3400XT (P1) 8440-2084
-
Woodward 8440-2082 EasyGen 3200XT Genset Controller
-
Woodward: easYgen-3200XT (P1/LT) 8440-2083
-
Woodward: easYgen-3100XT 8440-2081
-
Woodward: easYgen-2500 (1A/P1) K33 8440-2096
-
Woodward easYgen-2500-5/P1-K33 Rental Version 8440-2029
-
Woodward easYgen-2500-1/P1 8440-1860
-
Woodward easYgen-2500-5/P1 8440-1884
-
Woodward easYgen-2300-1/P2 8440-2123 Controller
-
Woodward easYgen-2300-5/P2 8440-2058
-
Woodward 2300E – Ordinary Locations 8273-1017
-
Woodward Vertex Compressor Control 8200-1370
-
MicroNet Safety Module - Bulkhead Mount 8237-2492 Woodward
-
ProTech TPS - Bulkhead Mount Independent Relays 8237-2602
-
Woodward ProTech-GII - Bulkhead Mount Independent Relays 8237-2594
-
ABB AX410, AX411, AX413, AX416, AX418, AX450, AX455 and AX456 Single and dual input analyzers for low level conductivity
-
ABB AX411/511010/STD Single and dual input analyzers
-
Woodward ProTech-SX - Panel Mount, HV/LV 8237-1242 8237-1243
-
Woodward SPC Servo Position Controller 8200-226 8200-227
-
Woodward Peak200 – Bulkhead Mount, LV 8200-1500
-
Woodward 505HT for Pelton Turbines 8200-1400, 8200-1401
-
Woodward 2301E-HT Hydro (Francis Turbines) P/N 8237-2046
-
Woodward 8273-1013 8273-1014 Digital Electronic Load Sharing
-
Control Panel 9907-2024 Woodward
-
ABB REF630 UBFNAAABBBAZANBBXB Feeder Protection and Device
-
ABB PPD513 A2A-11165 High-performance controller
-
UniOP CP10G-04 CP10G-04-0045 Interface Module
-
UNIOP MKDR-04-0021 Monochrome LCD (with Contrast Control)
-
UNIOP eTOP03-0046 Monochrome LCD (STN)
-
UNIOP MKDR-16-TA-0045 HMI TOUCH SCREEN
-
UNIOP Operator Interface Display MD02R-04-0042
-
UniOP Display Screen eTOP20C-0050 eTOP20C
-
UniOp eTOP05-0045 eTOP05. eTOP05P Operator Interface Touch Panel
-
UNIOP ETOP11-0050 HMI 5.6Color Operator Interface Touch Panel
-
UniOp eTOP306 Panel
-
UniOP eTOP308 ETOP308U301 HMI Panel
-
UniOP ePALM10-0061 Handheld Robot Trainer
-
UniOP CP01R-04 CP05R-04 and CP01F-02
-
Uniop MD02R-04 - MD02R-04-0045 Industrial PLC Workstation
-
Uniop Cp02r-04-0021 Operating Interface
-
UniOP ECT-16-0045 High-Performance Color Touchscreen HMI
-
UniOP ERT-16 - Industrial PLC Workstation
-
UniOP ePAD04-0046 Compact Industrial Interface
-
UniOP BKDR-16 High-Reliability Monochrome Operator Interface
-
UniOP MKDR-04-004 Control Unit Panel
-
UniOP eTOP515 Series 500 HMI
-
Woodward 9907-1199 Advanced CPC-II Current-to-Pressure Converter
-
Woodward 8200-1300 High-Precision 505D Steam Turbine Controller
-
ABB PFSK130 3BSE002616R1 Core Signal Conditioning Unit
-
ABB PFSK165 3BSE027778R1 VP74201-933CW07 Signal Processing and Communication Unit
-
ABB PFSK164 3BSE021180R1 Tension sensor module and processing board
-
ABB 3BSE006505R1 PFSK142 Control board
-
ABB PFSK160A 3BSE009514R1 Regulated High-Capacity 24V DC
-
ABB PFSK162 3BSE015088R1 Signal Conditioning and Processing Board
-
ABB PFSK152 3BSE018877R1 Signal concentrator board
-
ABB PFSK151 3BSE018876R1 High-performance signal processing unit
-
ALSTOM PIB1201A 3BEC0067 Power Interface Board (PIB)
-
ALSTOM PIB310 3BHB0190 Adapter Module / Printed Circuit Board (PCB)
-
ALSTOM PIB102A 3BEB0180 Communication Card / PCB Module
-
ALSTOM BGTR8HE 24491276A1004 High-Frequency Power Controller / Rack Module
-
ALSTOM LC105A-1 Digital Discrete Output (Relay)
-
ALSTOM IR139-1 High-Efficiency Inverter / Control Board
-
ALSTOM AM164 Analog Output / Remote I/O
-
ALSTOM LE109A-1 Power System Control and Monitoring Module
-
ALSTOM UT150-1 PID temperature controller / process control board
-
ALSTOM AL132 AL132A STO0982E01 Control Motherboard / CPU Card
-
ALSTOM AS111-1 Analog Output (AO) Module
-
WATLOW AH116-2 Servo Drive / Control Module
-
WATLOW V4555724-0100 Electromechanical Contactor /Power Switch
-
Alstom KCEU142 Digital Protection Relay
-
ALSTOM MMLG01 Test block
Add: High-tech Software Park, Xiamen City, Fujian Province
Mobile: +86-17750019513(WhatsApp)
Email: yy4291644@gmail.com
Website: https://www.abb-sis.com

-
Woodward easYgen-3200-1/P1 8440-2049
-
Woodward easYPROTEC-1410-7 8441-1161 8441-1160
-
Woodward MFR300-71M/K45 8444-1111 8444-1112
-
Woodward MFR300-75M 8444-1107 8444-1108 8444-1109
-
Woodward MFR300-71M/K42 8444-1104




.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)
.jpg)